Covalent Bonding Explained Notes (O Level + IGCSE + AQA + Edexcel)
Master Dot-and-Cross Diagrams and Simple Molecular Structure Properties for Guaranteed Marks.
Quick Access A*-Grade Study Resources (Internal Links):
Definitive A* Lecture Notes (2026-2027 Syllabus) | Organic Chemistry (Pillars) Chapter | Full IGCSE/O Level Chemistry Crash Course | O Level Chemistry Formula Sheet PDF (Molarity Formula Chemistry Calculator) | Past Paper Analysis (Ultra Premium Notes) | A* Action Plan Tips (Study for Chemistry O Level)1. The Concise, Exam-Centred Definition of Covalent Bonding
The foundation of all **Organic Chemistry** and simple molecules rests on this definition. Examiners look for specific keywords!
Covalent Bond Definition (Concise & Exam-Ready)
A **Covalent Bond** is the strong electrostatic force of attraction between the nuclei of two non-metal atoms and the **shared pair(s) of electrons** between them.
It is formed by the **sharing of valence electrons** between non-metal atoms, allowing each atom to achieve a stable, full outer electron shell (noble gas configuration).
This bond forms the basis of organic chemistry types of formulas like $\mathbf{CH_4}$ (Methane) and $\mathbf{H_2O}$ (Water).
2. Mastering Dot-and-Cross Diagrams (Essential for Paper 2/4)
Dot-and-cross diagrams are the primary way examiners test your understanding of covalent structure. Here's the most useful tip:
Dot-and-Cross Diagram Tip (The 'Sharing Circle' Rule)
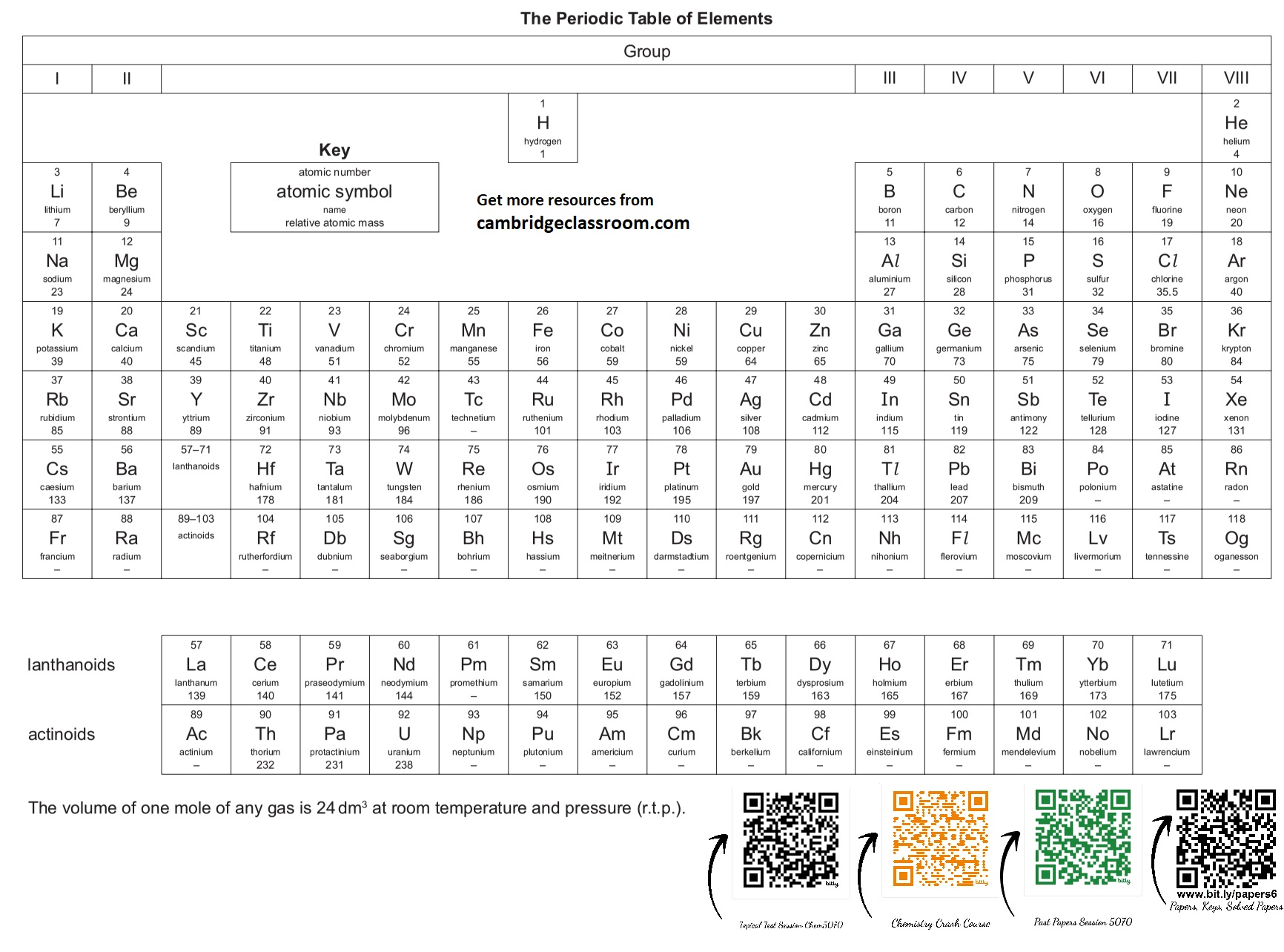
1. **Count Valence Electrons:** Determine the number of electrons in the outermost shell for each atom (use your Periodic Table Chapter knowledge).
2. **Identify Electrons Needed:** Calculate how many electrons each non-metal needs to achieve a noble gas configuration (usually 8).
3. **Draw Overlapping Circles:** The number of shared electrons must ensure all circles contain the stable number (e.g., 8 for most, 2 for Hydrogen). Use a distinct **dot and cross** to differentiate the origin of the electrons.
4. **Label Clearly:** The diagram must clearly show which type of formula shows an element symbol and the correct arrangement of shared and unshared electrons.
For more basic bonding concepts and the Periodic Table foundation, check out the video below:
3. Key Properties of Covalent Structures
Unlike the high melting points of ionic compounds, the weak forces in most covalent structures lead to different properties:
- **Low Melting and Boiling Points (Simple Molecular Structures):** Only a small amount of energy is needed to break the **weak intermolecular forces** (IMF) between the molecules. The strong covalent bond *within* the molecule is usually unaffected.
- **Non-Conductivity:** Covalent molecules contain no free electrons or mobile ions to carry an electric charge.
- **Solubility:** Non-polar covalent substances typically dissolve in non-polar solvents (e.g., oil in petrol). Polar covalent substances (like sugar) may dissolve in water.
🧑🏫 Teacher Profile: Prof. Faisal Janjowa (The Chemistry Guru)
Prof. Faisal Janjowa is dedicated to helping students master concepts like **understanding chemical formulas pdf** and complex structures. His Crash Course is tailored for students aiming for A* in O Level, IGCSE, AQA, and Edexcel Chemistry.
👉 **Live Class Details:** Join our next **Live Class** on **Chemical Energetics** to apply bonding knowledge to exothermic and endothermic reactions. Secure your enrollment in the Crash Course now!
4. Covalent Bonding in Practice: Past Paper Application
Practice makes perfect. These solved past paper videos show you exactly how to tackle complex bonding questions in your exam, linking the theory to the correct **chemical formula worksheet pdf** structure.
IGCSE 0620 Past Paper Solved (Bonding Diagrams and Properties)
O Level 5070 Past Paper Solved (Structure and Properties)
5. Your Covalent Bonding Study Timeline
- **Day 1-2 (Foundation):** Review the difference between ionic and covalent bonding. Master all Groups 1-8 valencies.
- **Day 3-4 (Diagrams):** Practice dot-and-cross diagrams for diatomic molecules ($\mathbf{O_2}$, $\mathbf{N_2}$) and compounds ($\mathbf{CH_4}$, $\mathbf{CO_2}$). Refer to your **high school chemistry formula sheet pdf**.
- **Day 5 (Properties):** Memorize the low M.P./B.P. and non-conductivity reasons. Study giant molecular structures like Silicon Dioxide.
- **Day 6+ (Application):** Start the Organic Chemistry Chapter (the largest application of covalent bonds) and apply your knowledge to past paper tips.